ManagedSignalR 1.0.0
dotnet add package ManagedSignalR --version 1.0.0
NuGet\Install-Package ManagedSignalR -Version 1.0.0
<PackageReference Include="ManagedSignalR" Version="1.0.0" />
<PackageVersion Include="ManagedSignalR" Version="1.0.0" />
<PackageReference Include="ManagedSignalR" />
paket add ManagedSignalR --version 1.0.0
#r "nuget: ManagedSignalR, 1.0.0"
#:package ManagedSignalR@1.0.0
#addin nuget:?package=ManagedSignalR&version=1.0.0
#tool nuget:?package=ManagedSignalR&version=1.0.0
🚀 ManagedSignalR
A powerful .NET library that provides a structured, topic-based approach to SignalR hub management with automatic command routing, custom serialization, and clean separation of concerns.
🔄 Communication Flow
ManagedSignalR supports two message flows :
InvokeServer(topic, payload)(implemented in the server-side library) – Client-to-Server communication, where the client sends a message to the server with a specified topic and serialized payload.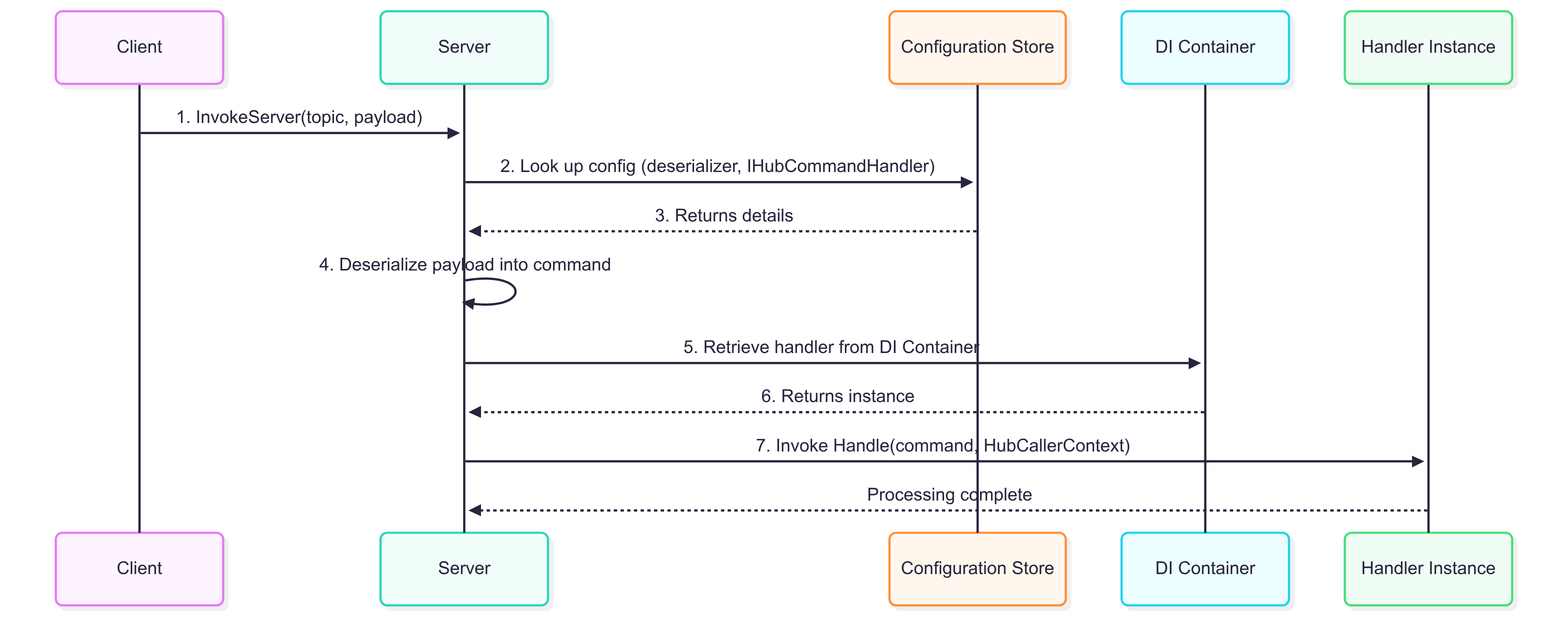
InvokeClient(topic, payload)(implemented on the client) – Server-to-Client communication. Do not call this directly in your application code; instead, useTryInvokeClientAsync(message)to ensure correct routing and serialization.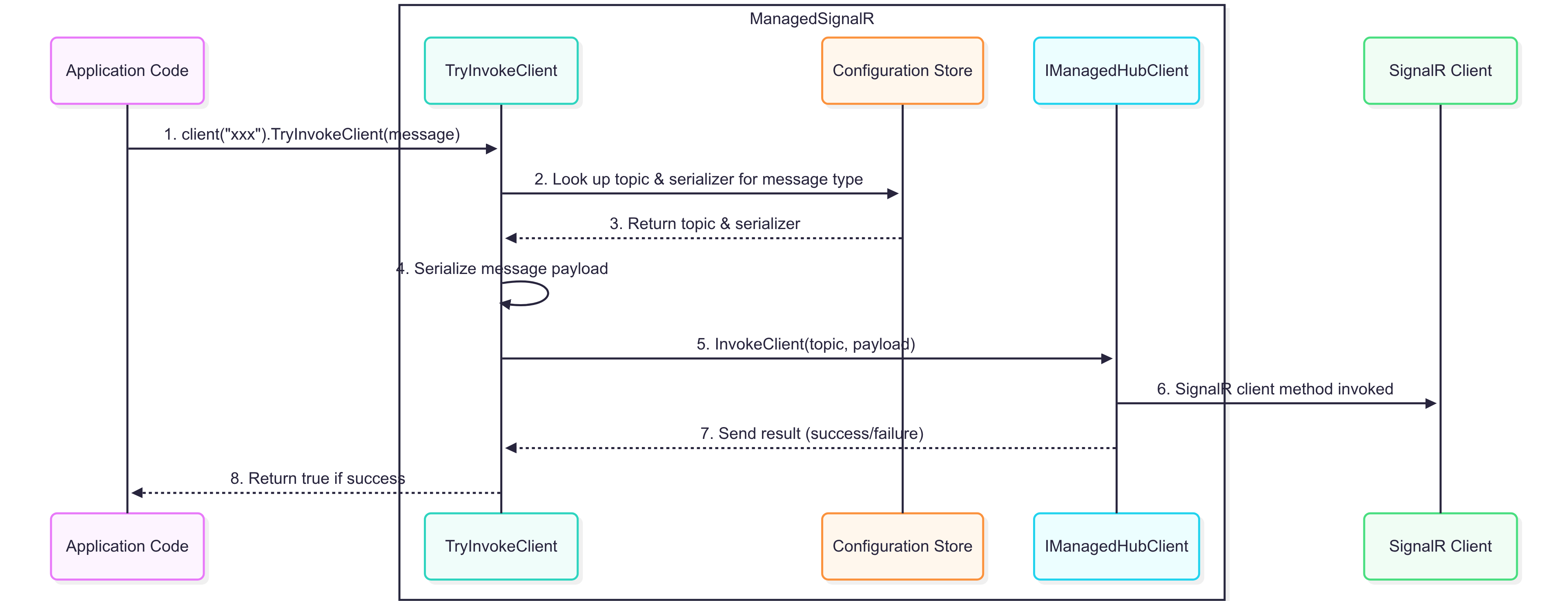
✨ Features
- 🎯 Topic-Based Routing: Route messages using string topics instead of method names
- 🧩 Command Handler Pattern: Clean separation of message handling logic using dedicated handler classes automatically registered via DI
- ⚡ Flexible Serialization: Support for custom serializers and deserializers per message type
- 🔒 Type-Safe Client Communication: Strongly typed messaging with automatic topic resolution
- 🔄 Connection Lifecycle Hooks: Override-friendly connection and disconnection event handling
- 🌐 Managed Hub Context: Access hub functionality from outside the hub using
IManagedHubContext<THub>instead ofIHubContext<THub, IManagedHubClient> - 🚀 Fire-and-Forget Processing: Asynchronous command processing with built-in error handling
📦 Installation
Install the package via NuGet:
dotnet add package ManagedSignalR
🏁 Quick Start
In your Startup.cs or Program.cs, configure the ManagedSignalR services:
builder.Services.AddManagedSignalR(config =>
{
/* FIRST HUB */
config.AddManagedHub<AppHub>()
// Configure outgoing messages (server to client)
.ConfigureInvokeClient<Alert>(cfg =>
cfg.RouteToTopic("alert")
.UseSerializer(obj => JsonSerializer.Serialize(obj)))
// Configure incoming messages (client to server)
.ConfigureInvokeServer<Coordinates>(cfg =>
cfg.OnTopic("gps")
// coordinates are received as "lat,long"
.UseDeserializer(str =>
{
var parts = str.Split(',');
return new Coordinates
{
Latitude = double.Parse(parts[0]), // assuming the 1st part is latitude
Longitude = double.Parse(parts[1]) // assuming the 2nd part is longitude
};
})
.UseHandler<CoordinatesHandler>())
.ConfigureInvokeClient<Message>(cfg =>
// Configure outgoing messages (server to client) for "msg" topic
// do not specify a serializer, it will use the default JSON serializer
cfg.RouteToTopic("msg"));
/* SECOND HUB */
//config.AddManagedHub<ChatHub>()...
});
Not to forget the default SignalR registration :
builder.Services.AddSignalR();
// add Redis backplane for distributed SignalR ...
2. Create Your Hub
Implement your hub by inheriting from ManagedHub. You can choose to override the connection lifecycle hooks for OnConnectedHookAsync and OnDisconnectedHookAsyncto run custom logic when clients connect or disconnect.
public class AppHub : ManagedHub
{
protected override async Task OnConnectedHookAsync()
{
var connectionId = Context.ConnectionId;
// Determine Early or Late group based on current time
var now = DateTime.Now;
string timeGroup = now.Hour < 12 ? "EarlyUsers" : "LateUsers";
// Add user to groups
await Groups.AddToGroupAsync(connectionId, timeGroup);
var alert = new Alert()
{
Content = $"Welcome! You belong within our {timeGroup} group"
};
// Optionally send a welcome message
await Clients.Caller.TryInvokeClientAsync(alert);
}
protected override async Task OnDisconnectedHookAsync()
{
var connectionId = Context.ConnectionId;
// Remove from all possible groups
await Groups.RemoveFromGroupAsync(connectionId, "EarlyUsers");
await Groups.RemoveFromGroupAsync(connectionId, "LateUsers");
}
}
3. Create Message Handlers
IHubCommandHandler<> command handlers are instantiated to handle incoming commands once they have been deserialized. These are automatically registered with the dependency injection container and can receive injected dependencies:
public class CoordinatesHandler : IHubCommandHandler<Coordinates>
{
private readonly IManagedHubContext<AppHub> _hubContext;
public CoordinatesHandler(IManagedHubContext<AppHub> hubContext)
{
_hubContext = hubContext;
}
public async Task Handle(Coordinates request, HubCallerContext context)
{
Console.WriteLine($"User {context.UserIdentifier} is at {request.Latitude}, {request.Longitude}");
var message = new Message
{
Text = $"Location received successfully! ({request.Latitude},{request.Longitude})"
};
// use IManagedHubContext<> to invoke client
await _hubContext.Clients.Client(context.ConnectionId).TryInvokeClientAsync(message);
}
}
4. Map Your Hub
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapHub<AppHub>("/apphub");
});
Usage
Client-Side Communication
From JavaScript/TypeScript:
const connection = new signalR.HubConnectionBuilder()
.withUrl("/apphub")
.build();
// Listen for messages from server
connection.on("InvokeClient", (topic, payload) => {
switch (topic) {
case "alert":
const alert = JSON.parse(payload);
console.log(`ALERT!!!\t${alert?.Content}`);
break;
case "msg":
const msg = JSON.parse(payload);
console.log(`NEW MESSAGE*\t${msg?.Text}`);
break;
default:
console.log(`[unexpected topic]\t${topic} => ${payload}`);
break;
}
});
// Send message to server
connection.invoke("InvokeServer", "gps", "40.7128,-74.0060");
connection.start();
Accessing Hub from Other Code
To access hub functionality from controllers, services, or other parts of your application, inject IManagedHubContext<THub> instead of the default SignalR IHubContext<THub, IManagedHubClient>:
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class NotificationController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IManagedHubContext<AppHub> _hubContext;
public NotificationController(IManagedHubContext<AppHub> hubContext)
{
_hubContext = hubContext;
}
[HttpPost("broadcast")]
public async Task<IActionResult> BroadcastAlert([FromBody] Alert alert)
{
await _hubContext.Clients.All.TryInvokeClientAsync(alert);
return Ok();
}
}
Configuration Options
Serialization
Configure custom serializers for outgoing messages:
.ConfigureInvokeClient<MyMessage>(cfg =>
cfg.RouteToTopic("my-topic")
.UseSerializer(obj => MyCustomSerializer.Serialize(obj)))
Deserialization
Configure custom deserializers for incoming messages:
.ConfigureInvokeServer<MyCommand>(cfg =>
cfg.OnTopic("my-command")
.UseDeserializer(json => MyCustomDeserializer.Deserialize<MyCommand>(json))
.UseHandler<MyCommandHandler>())
Default JSON Serialization
If no custom serializer is specified, System.Text.Json is used by default:
.ConfigureInvokeClient<Message>(cfg =>
cfg.RouteToTopic("message")) // Uses default JSON serialization
Advanced Features
Connection Lifecycle
Override connection hooks for custom logic:
public class AppHub : ManagedHub
{
protected override async Task OnConnectedHookAsync()
{
var connectionId = Context.ConnectionId;
// Determine Early or Late group based on current time
var now = DateTime.Now;
string timeGroup = now.Hour < 12 ? "EarlyUsers" : "LateUsers";
// Add user to groups
await Groups.AddToGroupAsync(connectionId, timeGroup);
var alert = new Alert()
{
Content = $"Welcome! You belong within our {timeGroup} group"
};
// Optionally send a welcome message
await Clients.Caller.TryInvokeClientAsync(alert);
}
protected override async Task OnDisconnectedHookAsync()
{
var connectionId = Context.ConnectionId;
// Remove from all possible groups
await Groups.RemoveFromGroupAsync(connectionId, "EarlyUsers");
await Groups.RemoveFromGroupAsync(connectionId, "LateUsers");
}
}
Requirements
- .NET 8.0 or later
- Microsoft.AspNetCore.SignalR
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
Examples
For more examples and usage patterns, check out the /examples folder in the repository.
ManagedSignalR - Making SignalR hubs more manageable, one topic at a time! 🚀
| Product | Versions Compatible and additional computed target framework versions. |
|---|---|
| .NET | net8.0 is compatible. net8.0-android was computed. net8.0-browser was computed. net8.0-ios was computed. net8.0-maccatalyst was computed. net8.0-macos was computed. net8.0-tvos was computed. net8.0-windows was computed. net9.0 was computed. net9.0-android was computed. net9.0-browser was computed. net9.0-ios was computed. net9.0-maccatalyst was computed. net9.0-macos was computed. net9.0-tvos was computed. net9.0-windows was computed. net10.0 was computed. net10.0-android was computed. net10.0-browser was computed. net10.0-ios was computed. net10.0-maccatalyst was computed. net10.0-macos was computed. net10.0-tvos was computed. net10.0-windows was computed. |
-
net8.0
- Microsoft.AspNetCore.SignalR (>= 1.2.0)
NuGet packages
This package is not used by any NuGet packages.
GitHub repositories
This package is not used by any popular GitHub repositories.
| Version | Downloads | Last Updated |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0.0 | 137 | 8/15/2025 |