ChatGptNet 3.2.18
See the version list below for details.
dotnet add package ChatGptNet --version 3.2.18
NuGet\Install-Package ChatGptNet -Version 3.2.18
<PackageReference Include="ChatGptNet" Version="3.2.18" />
paket add ChatGptNet --version 3.2.18
#r "nuget: ChatGptNet, 3.2.18"
// Install ChatGptNet as a Cake Addin #addin nuget:?package=ChatGptNet&version=3.2.18 // Install ChatGptNet as a Cake Tool #tool nuget:?package=ChatGptNet&version=3.2.18
ChatGPT for .NET
A ChatGPT integration library for .NET, supporting both OpenAI and Azure OpenAI Service.
Installation
The library is available on NuGet. Just search for ChatGptNet in the Package Manager GUI or run the following command in the .NET CLI:
dotnet add package ChatGptNet
Configuration
Register ChatGPT service at application startup:
builder.Services.AddChatGpt(options =>
{
// OpenAI.
//options.UseOpenAI(apiKey: "", organization: "");
// Azure OpenAI Service.
//options.UseAzure(resourceName: "", apiKey: "", authenticationType: AzureAuthenticationType.ApiKey);
options.DefaultModel = "my-model";
options.DefaultEmbeddingModel = "text-embedding-ada-002";
options.MessageLimit = 16; // Default: 10
options.MessageExpiration = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(5); // Default: 1 hour
options.DefaultParameters = new ChatGptParameters
{
MaxTokens = 800,
Temperature = 0.7
};
});
ChatGptNet supports both OpenAI and Azure OpenAI Service, so it is necessary to set the correct configuration settings based on the chosen provider:
OpenAI (UseOpenAI)
- ApiKey: it is available in the User settings page of the OpenAI account (required).
- Organization: for users who belong to multiple organizations, you can also specify which organization is used. Usage from these API requests will count against the specified organization's subscription quota (optional).
Azure OpenAI Service (UseAzure)
- ResourceName: the name of your Azure OpenAI Resource (required).
- ApiKey: Azure OpenAI provides two methods for authentication. You can use either API Keys or Azure Active Directory (required).
- ApiVersion: the version of the API to use (optional). Allowed values:
- 2023-05-15
- 2023-06-01-preview
- 2023-10-01-preview
- 2024-02-15-preview
- 2024-03-01-preview
- 2024-04-01-preview
- 2024-05-01-preview
- 2024-02-01
- 2024-06-01 (default)
- AuthenticationType: it specifies if the key is an actual API Key or an Azure Active Directory token (optional, default: "ApiKey").
DefaultModel and DefaultEmbeddingModel
ChatGPT can be used with different models for chat completion, both on OpenAI and Azure OpenAI service. With the DefaultModel property, you can specify the default model that will be used, unless you pass an explicit value in the AskAsync or AsyStreamAsync methods.
Even if it is not a strictly necessary for chat conversation, the library supports also the Embedding API, on both OpenAI and Azure OpenAI. As for chat completion, embeddings can be done with different models. With the DefaultEmbeddingModel property, you can specify the default model that will be used, unless you pass an explicit value in the GetEmbeddingAsync method.
OpenAI
Currently available models are:
- gpt-3.5-turbo,
- gpt-3.5-turbo-16k,
- gpt-4,
- gpt-4-32k
- gpt-4-turbo
- gpt-4o
- gpt-4o-mini
They have fixed names, available in the OpenAIChatGptModels.cs file.
Azure OpenAI Service
In Azure OpenAI Service, you're required to first deploy a model before you can make calls. When you deploy a model, you need to assign it a name, that must match the name you use with ChatGptNet.
Note Some models are not available in all regions. You can refer to Model Summary table and region availability page to check current availabilities.
Caching, MessageLimit and MessageExpiration
ChatGPT is aimed to support conversational scenarios: user can talk to ChatGPT without specifying the full context for every interaction. However, conversation history isn't managed by OpenAI or Azure OpenAI service, so it's up to us to retain the current state. By default, ChatGptNet handles this requirement using a MemoryCache that stores messages for each conversation. The behavior can be set using the following properties:
- MessageLimit: specifies how many messages for each conversation must be saved. When this limit is reached, oldest messages are automatically removed.
- MessageExpiration: specifies the time interval used to maintain messages in cache, regardless their count.
If necessary, it is possibile to provide a custom Cache by implementing the IChatGptCache interface and then calling the WithCache extension method:
public class LocalMessageCache : IChatGptCache
{
private readonly Dictionary<Guid, IEnumerable<ChatGptMessage>> localCache = new();
public Task SetAsync(Guid conversationId, IEnumerable<ChatGptMessage> messages, TimeSpan expiration, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
localCache[conversationId] = messages.ToList();
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
public Task<IEnumerable<ChatGptMessage>?> GetAsync(Guid conversationId, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
localCache.TryGetValue(conversationId, out var messages);
return Task.FromResult(messages);
}
public Task RemoveAsync(Guid conversationId, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
localCache.Remove(conversationId);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
public Task<bool> ExistsAsync(Guid conversationId, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
var exists = localCache.ContainsKey(conversationId);
return Task.FromResult(exists);
}
}
// Registers the custom cache at application startup.
builder.Services.AddChatGpt(/* ... */).WithCache<LocalMessageCache>();
We can also set ChatGPT parameters for chat completion at startup. Check the official documentation for the list of available parameters and their meaning.
Configuration using an external source
The configuration can be automatically read from IConfiguration, using for example a ChatGPT section in the appsettings.json file:
"ChatGPT": {
"Provider": "OpenAI", // Optional. Allowed values: OpenAI (default) or Azure
"ApiKey": "", // Required
//"Organization": "", // Optional, used only by OpenAI
"ResourceName": "", // Required when using Azure OpenAI Service
"ApiVersion": "2024-06-01", // Optional, used only by Azure OpenAI Service (default: 2024-06-01)
"AuthenticationType": "ApiKey", // Optional, used only by Azure OpenAI Service. Allowed values: ApiKey (default) or ActiveDirectory
"DefaultModel": "my-model",
"DefaultEmbeddingModel": "text-embedding-ada-002", // Optional, set it if you want to use embedding
"MessageLimit": 20,
"MessageExpiration": "00:30:00",
"ThrowExceptionOnError": true // Optional, default: true
//"User": "UserName",
//"DefaultParameters": {
// "Temperature": 0.8,
// "TopP": 1,
// "MaxTokens": 500,
// "PresencePenalty": 0,
// "FrequencyPenalty": 0,
// "ResponseFormat": { "Type": "text" }, // Allowed values for Type: text (default) or json_object
// "Seed": 42 // Optional (any integer value)
//},
//"DefaultEmbeddingParameters": {
// "Dimensions": 1536
//}
}
And then use the corresponding overload of che AddChatGpt method:
// Adds ChatGPT service using settings from IConfiguration.
builder.Services.AddChatGpt(builder.Configuration);
Configuring ChatGptNet dinamically
The AddChatGpt method has also an overload that accepts an IServiceProvider as argument. It can be used, for example, if we're in a Web API and we need to support scenarios in which every user has a different API Key that can be retrieved accessing a database via Dependency Injection:
builder.Services.AddChatGpt((services, options) =>
{
var accountService = services.GetRequiredService<IAccountService>();
// Dynamically gets the API Key from the service.
var apiKey = "..."
options.UseOpenAI(apiKyey);
});
Configuring ChatGptNet using both IConfiguration and code
In more complex scenarios, it is possible to configure ChatGptNet using both code and IConfiguration. This can be useful if we want to set a bunch of common properties, but at the same time we need some configuration logic. For example:
builder.Services.AddChatGpt((services, options) =>
{
// Configure common properties (message limit and expiration, default parameters, ecc.) using IConfiguration.
options.UseConfiguration(builder.Configuration);
var accountService = services.GetRequiredService<IAccountService>();
// Dynamically gets the API Key from the service.
var apiKey = "..."
options.UseOpenAI(apiKyey);
});
Configuring HTTP Client
ChatGptNet uses an HttpClient to call the chat completion and embedding APIs. If you need to customize it, you can use the overload of the AddChatGpt method that accepts an Action<IHttpClientBuiler> as argument. For example, if you want to add resiliency to the HTTP client (let's say a retry policy), you can use Polly:
// using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
// Requires: Microsoft.Extensions.Http.Resilience
builder.Services.AddChatGpt(context.Configuration,
httpClient =>
{
// Configures retry policy on the inner HttpClient using Polly.
httpClient.AddStandardResilienceHandler(options =>
{
options.AttemptTimeout.Timeout = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1);
options.CircuitBreaker.SamplingDuration = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(3);
options.TotalRequestTimeout.Timeout = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(3);
});
})
More information about this topic is available on the official documentation.
Usage
The library can be used in any .NET application built with .NET 6.0 or later. For example, we can create a Minimal API in this way:
app.MapPost("/api/chat/ask", async (Request request, IChatGptClient chatGptClient) =>
{
var response = await chatGptClient.AskAsync(request.ConversationId, request.Message);
return TypedResults.Ok(response);
})
.WithOpenApi();
// ...
public record class Request(Guid ConversationId, string Message);
If we just want to retrieve the response message, we can call the GetContent method:
var content = response.GetContent();
Note If the response has been filtered by the content filtering system, GetContent will return null. So, you should always check the
response.IsContentFilteredproperty before trying to access to the actual content.
Using parameters
Using configuration, it is possible to set default parameters for chat completion. However, we can also specify parameters for each request, using the AskAsync or AskStreamAsync overloads that accepts a ChatGptParameters object:
var response = await chatGptClient.AskAsync(conversationId, message, new ChatGptParameters
{
MaxTokens = 150,
Temperature = 0.7
});
We don't need to specify all the parameters, only the ones we want to override. The other ones will be taken from the default configuration.
Seed and system fingerprint
ChatGPT is known to be non deterministic. This means that the same input can produce different outputs. To try to control this behavior, we can use the Temperature and TopP parameters. For example, setting the Temperature to values near to 0 makes the model more deterministic, while setting it to values near to 1 makes the model more creative. However, this is not always enough to get the same output for the same input. To address this issue, OpenAI introduced the Seed parameter. If specified, the model should sample deterministically, such that repeated requests with the same seed and parameters should return the same result. Nevertheless, determinism is not guaranteed neither in this case, and you should refer to the SystemFingerprint response parameter to monitor changes in the backend. Changes in this values mean that the backend configuration has changed, and this might impact determinism.
As always, the Seed property can be specified in the default configuration or in the AskAsync or AskStreamAsync overloads that accepts a ChatGptParameters.
Note Seed and SystemFingerprint are only supported by the most recent models, such as gpt-4-1106-preview.
Response format
If you want to forse the response in JSON format, you can use the ResponseFormat parameter:
var response = await chatGptClient.AskAsync(conversationId, message, new ChatGptParameters
{
ResponseFormat = ChatGptResponseFormat.Json,
});
In this way, the response will always be a valid JSON. Note that must also instruct the model to produce JSON via a system or user message. If you don't do this, the model will return an error.
As always, the ResponseFormat property can be specified in the default configuration or in the AskAsync or AskStreamAsync overloads that accepts a ChatGptParameters.
Note ResponseFormat is only supported by the most recent models, such as gpt-4-1106-preview.
Handling a conversation
The AskAsync and AskStreamAsync (see below) methods provides overloads that require a conversationId parameter. If we pass an empty value, a random one is generated and returned. We can pass this value in subsequent invocations of AskAsync or AskStreamAsync, so that the library automatically retrieves previous messages of the current conversation (according to MessageLimit and MessageExpiration settings) and send them to chat completion API.
This is the default behavior for all the chat interactions. If you want to exlude a particular interaction from the conversation history, you can set the addToConversationHistory argument to false:
var response = await chatGptClient.AskAsync(conversationId, message, addToConversationHistory: false);
In this way, the message will be sent to the chat completion API, but it and the corresponding answer from ChatGPT will not be added to the conversation history.
On the other hand, in some scenarios, it could be useful to manually add a chat interaction (i.e., a question followed by an answer) to the conversation history. For example, we may want to add a message that was generated by a bot. In this case, we can use the AddInteractionAsync method:
await chatGptClient.AddInteractionAsync(conversationId, question: "What is the weather like in Taggia?",
answer: "It's Always Sunny in Taggia");
The question will be added as user message and the answer will be added as assistant message in the conversation history. As always, these new messages (respecting the MessageLimit option) will be used in subsequent invocations of AskAsync or AskStreamAsync.
Response streaming
Chat completion API supports response streaming. When using this feature, partial message deltas will be sent, like in ChatGPT. Tokens will be sent as data-only server-sent events as they become available. ChatGptNet provides response streaming using the AskStreamAsync method:
// Requests a streaming response.
var responseStream = chatGptClient.AskStreamAsync(conversationId, message);
await foreach (var response in responseStream)
{
Console.Write(response.GetContent());
await Task.Delay(80);
}

Note If the response has been filtered by the content filtering system, the GetContent method in the foreach will return null strings. So, you should always check the
response.IsContentFilteredproperty before trying to access to the actual content.
Response streaming works by returning an IAsyncEnumerable, so it can be used even in a Web API project:
app.MapGet("/api/chat/stream", (Guid? conversationId, string message, IChatGptClient chatGptClient) =>
{
async IAsyncEnumerable<string?> Stream()
{
// Requests a streaming response.
var responseStream = chatGptClient.AskStreamAsync(conversationId.GetValueOrDefault(), message);
// Uses the "AsDeltas" extension method to retrieve partial message deltas only.
await foreach (var delta in responseStream.AsDeltas())
{
yield return delta;
await Task.Delay(50);
}
}
return Stream();
})
.WithOpenApi();
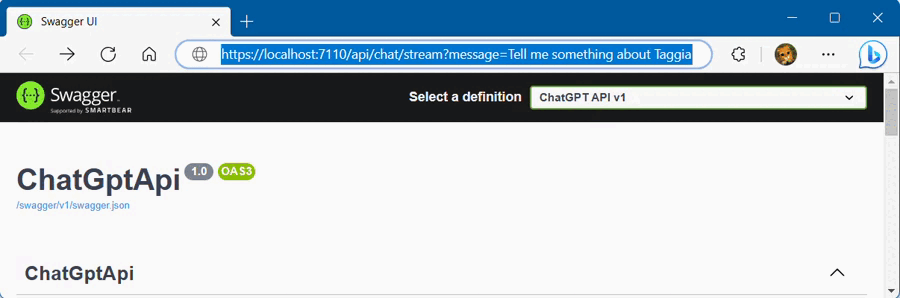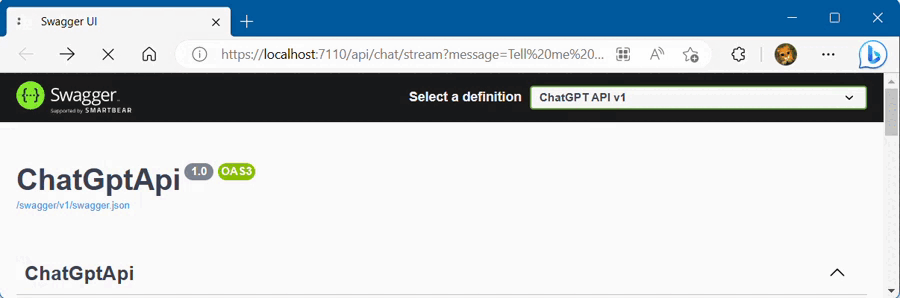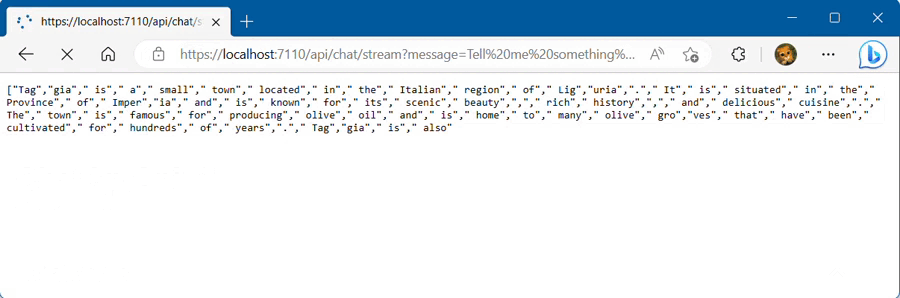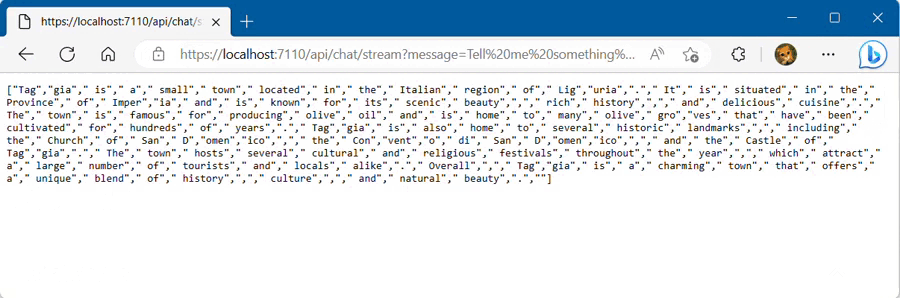
Note If the response has been filtered by the content filtering system, the AsDeltas method in the foreach will return nulls string.
The library is 100% compatible also with Blazor WebAssembly applications:
Check out the Samples folder for more information about the different implementations.
Changing the assistant's behavior
ChatGPT supports messages with the system role to influence how the assistant should behave. For example, we can tell to ChatGPT something like that:
- You are an helpful assistant
- Answer like Shakespeare
- Give me only wrong answers
- Answer in rhyme
ChatGptNet provides this feature using the SetupAsync method:
var conversationId await = chatGptClient.SetupAsync("Answer in rhyme");
If we use the same conversationId when calling AskAsync, then the system message will be automatically sent along with every request, so that the assistant will know how to behave.
Note The system message does not count for messages limit number.
Deleting a conversation
Conversation history is automatically deleted when expiration time (specified by MessageExpiration property) is reached. However, if necessary it is possible to immediately clear the history:
await chatGptClient.DeleteConversationAsync(conversationId, preserveSetup: false);
The preserveSetup argument allows to decide whether mantain also the system message that has been set with the SetupAsync method (default: false).
Tool and Function calling
With function calling, we can describe functions and have the model intelligently choose to output a JSON object containing arguments to call those functions. This is a new way to more reliably connect GPT's capabilities with external tools and APIs.
ChatGptNet fully supports function calling by providing an overload of the AskAsync method that allows to specify function definitions. If this parameter is supplied, then the model will decide when it is appropiate to use one the functions. For example:
var functions = new List<ChatGptFunction>
{
new()
{
Name = "GetCurrentWeather",
Description = "Get the current weather",
Parameters = JsonDocument.Parse("""
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and/or the zip code"
},
"format": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"],
"description": "The temperature unit to use. Infer this from the user's location."
}
},
"required": ["location", "format"]
}
""")
},
new()
{
Name = "GetWeatherForecast",
Description = "Get an N-day weather forecast",
Parameters = JsonDocument.Parse("""
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and/or the zip code"
},
"format": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"],
"description": "The temperature unit to use. Infer this from the user's location."
},
"daysNumber": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "The number of days to forecast"
}
},
"required": ["location", "format", "daysNumber"]
}
""")
}
};
var toolParameters = new ChatGptToolParameters
{
FunctionCall = ChatGptToolChoices.Auto, // This is the default if functions are present.
Functions = functions
};
var response = await chatGptClient.AskAsync("What is the weather like in Taggia?", toolParameters);
We can pass an arbitrary number of functions, each one with a name, a description and a JSON schema describing the function parameters, following the JSON Schema references. Under the hood, functions are injected into the system message in a syntax the model has been trained on. This means functions count against the model's context limit and are billed as input tokens.
The response object returned by the AskAsync method provides a property to check if the model has selected a function call:
if (response.ContainsFunctionCalls())
{
Console.WriteLine("I have identified a function to call:");
var functionCall = response.GetFunctionCall()!;
Console.WriteLine(functionCall.Name);
Console.WriteLine(functionCall.Arguments);
}
This code will print something like this:
I have identified a function to call:
GetCurrentWeather
{
"location": "Taggia",
"format": "celsius"
}
Note that the API will not actually execute any function calls. It is up to developers to execute function calls using model outputs.
After the actual execution, we need to call the AddToolResponseAsync method on the ChatGptClient to add the response to the conversation history, just like a standard message, so that it will be automatically used for chat completion:
// Calls the remote function API.
var functionResponse = await GetWeatherAsync(functionCall.Arguments);
await chatGptClient.AddToolResponseAsync(conversationId, functionCall, functionResponse);
Newer models like gpt-4-turbo support a more general approach to functions, the Tool calling. When you send a request, you can specify a list of tools the model may call. Currently, only functions are supported, but in future release other types of tools will be available.
To use Tool calling instead of direct Function calling, you need to set the ToolChoice and Tools properties in the ChatGptToolParameters object (instead of FunctionCall and Function, as in previous example):
var toolParameters = new ChatGptToolParameters
{
ToolChoice = ChatGptToolChoices.Auto, // This is the default if functions are present.
Tools = functions.ToTools()
};
The ToTools extension method is used to convert a list of ChatGptFunction to a list of tools.
If you use this new approach, of course you still need to check if the model has selected a tool call, using the same approach shown before. Then, after the actual execution of the function, you have to call the AddToolResponseAsync method, but in this case you need to specify the tool (not the function) to which the response refers:
var tool = response.GetToolCalls()!.First();
var functionCall = response.GetFunctionCall()!;
// Calls the remote function API.
var functionResponse = await GetWeatherAsync(functionCall.Arguments);
await chatGptClient.AddToolResponseAsync(conversationId, tool, functionResponse);
Finally, you need to resend the original message to the chat completion API, so that the model can continue the conversation taking into account the function call response. Check out the Function calling sample for a complete implementation of this workflow.
Content filtering
When using Azure OpenAI Service, we automatically get content filtering for free. For details about how it works, check out the documentation. This information is returned for all scenarios when using API version 2023-06-01-preview or later. ChatGptNet fully supports this object model by providing the corresponding properties in the ChatGptResponse and ChatGptChoice classes.
Embeddings
Embeddings allows to transform text into a vector space. This can be useful to compare the similarity of two sentences, for example. ChatGptNet fully supports this feature by providing the GetEmbeddingAsync method:
var response = await chatGptClient.GenerateEmbeddingAsync(message);
var embeddings = response.GetEmbedding();
This code will give you a float array containing all the embeddings for the specified message. The length of the array depends on the model used:
| Model | Output dimension |
|---|---|
| text-embedding-ada-002 | 1536 |
| text-embedding-3-small | 1536 |
| text-embedding-3-large | 3072 |
Newer models like text-embedding-3-small and text-embedding-3-large allows developers to trade-off performance and cost of using embeddings. Specifically, developers can shorten embeddings without the embedding losing its concept-representing properties.
As for ChatGPT, this settings can be done in various ways:
- Via code:
builder.Services.AddChatGpt(options =>
{
// ...
options.DefaultEmbeddingParameters = new EmbeddingParameters
{
Dimensions = 256
};
});
- Using the appsettings.json file:
"ChatGPT": {
"DefaultEmbeddingParameters": {
"Dimensions": 256
}
}
Then, if you want to change the dimension for a particular request, you can specify the EmbeddingParameters argument in the GetEmbeddingAsync invocation:
var response = await chatGptClient.GenerateEmbeddingAsync(request.Message, new EmbeddingParameters
{
Dimensions = 512
});
var embeddings = response.GetEmbedding(); // The length of the array is 512
If you need to calculate the cosine similarity between two embeddings, you can use the EmbeddingUtility.CosineSimilarity method.
Documentation
The full technical documentation is available here.
Contribute
The project is constantly evolving. Contributions are welcome. Feel free to file issues and pull requests on the repo and we'll address them as we can.
Warning Remember to work on the develop branch, don't use the master branch directly. Create Pull Requests targeting develop.
| Product | Versions Compatible and additional computed target framework versions. |
|---|---|
| .NET | net6.0 is compatible. net6.0-android was computed. net6.0-ios was computed. net6.0-maccatalyst was computed. net6.0-macos was computed. net6.0-tvos was computed. net6.0-windows was computed. net7.0 is compatible. net7.0-android was computed. net7.0-ios was computed. net7.0-maccatalyst was computed. net7.0-macos was computed. net7.0-tvos was computed. net7.0-windows was computed. net8.0 is compatible. net8.0-android was computed. net8.0-browser was computed. net8.0-ios was computed. net8.0-maccatalyst was computed. net8.0-macos was computed. net8.0-tvos was computed. net8.0-windows was computed. net9.0 was computed. net9.0-android was computed. net9.0-browser was computed. net9.0-ios was computed. net9.0-maccatalyst was computed. net9.0-macos was computed. net9.0-tvos was computed. net9.0-windows was computed. |
-
net6.0
- Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.Memory (>= 6.0.1)
- Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.Binder (>= 6.0.0)
- Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection.Abstractions (>= 6.0.0)
- Microsoft.Extensions.Http (>= 6.0.0)
-
net7.0
- Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.Memory (>= 7.0.0)
- Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.Binder (>= 7.0.4)
- Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection.Abstractions (>= 7.0.0)
- Microsoft.Extensions.Http (>= 7.0.0)
-
net8.0
- Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.Memory (>= 8.0.0)
- Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.Binder (>= 8.0.2)
- Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection.Abstractions (>= 8.0.1)
- Microsoft.Extensions.Http (>= 8.0.0)
NuGet packages
This package is not used by any NuGet packages.
GitHub repositories
This package is not used by any popular GitHub repositories.
| Version | Downloads | Last updated |
|---|---|---|
| 3.3.9 | 640 | 11/6/2024 |
| 3.3.7 | 100 | 11/5/2024 |
| 3.3.5 | 243 | 10/15/2024 |
| 3.3.4 | 602 | 9/11/2024 |
| 3.3.2 | 147 | 9/5/2024 |
| 3.2.18 | 297 | 7/23/2024 |
| 3.2.17 | 482 | 6/26/2024 |
| 3.2.15 | 1,465 | 5/17/2024 |
| 3.2.14 | 240 | 5/3/2024 |
| 3.2.10 | 1,236 | 3/13/2024 |
| 3.2.9 | 168 | 3/7/2024 |
| 3.2.2 | 396 | 1/29/2024 |
| 3.1.2 | 284 | 1/17/2024 |
| 3.0.7 | 253 | 1/8/2024 |
| 3.0.6 | 838 | 12/11/2023 |
| 2.6.3 | 1,545 | 10/16/2023 |
| 2.5.4 | 481 | 9/19/2023 |
| 2.4.7 | 283 | 9/18/2023 |
| 2.2.15 | 344 | 9/7/2023 |
| 2.2.14 | 522 | 8/11/2023 |
| 2.2.12 | 380 | 8/3/2023 |
| 2.2.11 | 283 | 7/27/2023 |
| 2.2.8 | 204 | 7/21/2023 |
| 2.2.4 | 183 | 7/20/2023 |
| 2.1.9 | 252 | 7/12/2023 |
| 2.1.6 | 266 | 6/26/2023 |
| 2.1.3 | 269 | 6/19/2023 |
| 2.0.16 | 230 | 6/14/2023 |
| 2.0.14 | 281 | 6/7/2023 |
| 2.0.11 | 204 | 6/5/2023 |
| 2.0.9 | 208 | 5/30/2023 |
| 2.0.3 | 310 | 5/16/2023 |
| 1.4.2 | 455 | 4/17/2023 |
| 1.3.8 | 260 | 4/10/2023 |
| 1.3.6 | 241 | 4/5/2023 |
| 1.3.3 | 268 | 3/29/2023 |
| 1.2.3 | 580 | 3/24/2023 |
| 1.1.6 | 269 | 3/22/2023 |
| 1.1.4 | 276 | 3/21/2023 |
| 1.0.5 | 274 | 3/19/2023 |
| 0.1.12 | 274 | 3/12/2023 |
| 0.1.8 | 250 | 3/11/2023 |


